Arthritis is a collective term that claims to describe over 100 different conditions described by inflammation and pain in the joints. The causes, effects, and treatments for these symptoms are all necessary to be managed effectively for this condition. In this blog post, we will discuss further the detailed symptoms of arthritis, its causes and effects, available treatments, and some home remedies that can help ease the symptoms.
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is generally the inflammation of one or more joints, which results in pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can be common among people of all ages, backgrounds, and lifestyles. The two most common types of arthritis are:
Osteoarthritis (OA): This is often also referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis. OA is created when the cartilage that cushions between the joints begins to deteriorate over time, hence causing the bone to rub against the bone.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: This is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the synovium or the joint lining. This usually leads to inflammation and destruction of the joints.
Common Arthritis Symptoms
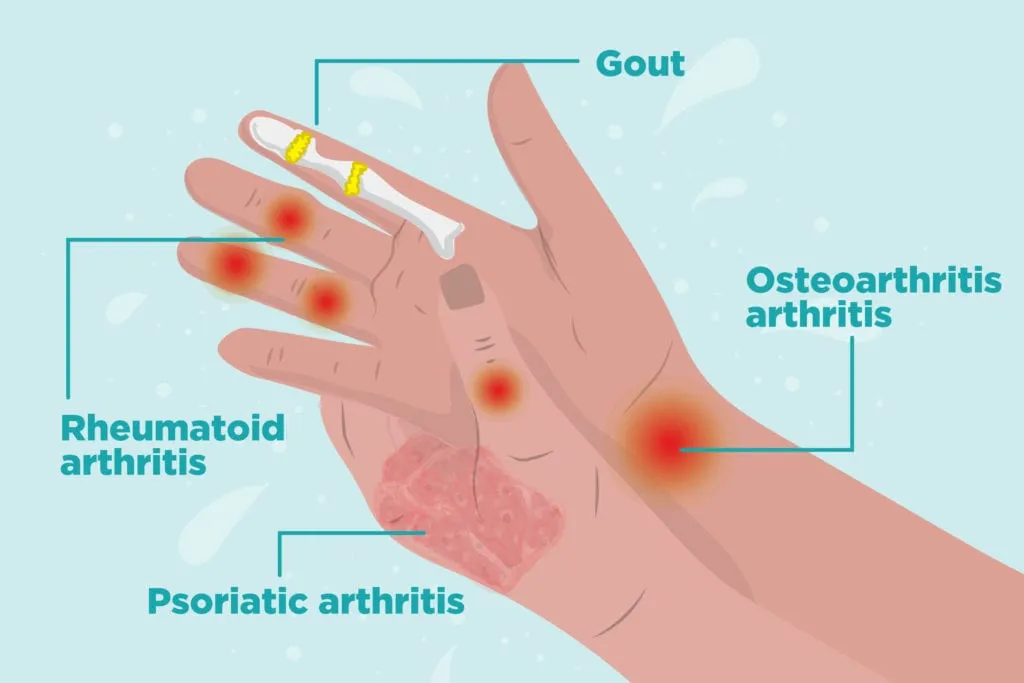
The symptoms of arthritis are different from one person to another. Some common symptoms depending on the type and severity of the condition are:
1. Joint Pain
It is also characterized by a marked pain in the affected joints. It ranges from mild to severe and often worsens about activity or by a pattern following long periods of rest.
2. Swelling
Swelling around the joints can also cause noticeable swelling. Sometimes, the skin over the joint may feel warm and appear red.
3. Stiffness
This is a very common symptom, with joint stiffness noted in many cases, especially upon rising and after prolonged sitting. This can naturally impact the movement of the involved joints.
4. Fatigue
For many people, chronic fatigue is part of the experience with arthritis. Pain and difficulty with sleep are also problems for many individuals with arthritis.
5. Decreased Range of Motion
Continued inflammation and pain may result in a decreased range of motion in those affected joints, which can limit many routine activities.
6. Crepitation
When the joint is moved, crepitus which is a grating or crackling sound may be present, especially in osteoarthritis.
7. Heat and Redness
The skin over the affected area may be warm to palpation and red because of inflammation.
8. Nodules
In rheumatoid arthritis, firm lumps called rheumatoid nodules may be present beneath the skin, particularly over bony prominences.
9. Systemic Symptoms
Besides the primary symptoms, swollen joints, joint pain, and stiffness, other symptoms may be fever, weight loss, and general malaise in autoimmune forms like rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes of Arthritis
Causes of arthritis differ according to the type. Some common causes for the disease are given below.
1. Genetics
Genetic predisposition is a cause of arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis. A family history of arthritis may increase your chance of getting the disease.
2. Age
There is an increased risk of osteoarthritis with age. The joints get worn out with time.
3. Sex
The female gender is at more risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, especially at childbearing ages.
4. History of Joint Trauma
An individual who has undergone cracking of the joints or tearing of the ligaments develops more chance of osteoarthritis later.
5. Obesity
Extra body weight exaggerates joint functionality, and among weight-bearing joints, it goes on to increase the chances of developing osteoarthritis.
6. Autoimmune Reactions
In conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system of the body attacks the joint tissues on a mistaken impression, leading to inflammation.
Effects of Arthritis
Physical symptoms of arthritis not only bring feelings of limitation but also influence emotional and mental states. Many experience the following effects:
1. Lowered Mobility
Pain and stiffness are constant reminders of reduced mobility; for example, when it becomes difficult to walk, climb the stairs, or even type.
2. Psychological Impact
Having chronic pain gives one frustration, sad feelings, and in extreme cases, depression. Once more, the impact brings about isolation in daily life.
3. Sleep Disorders
Ache and pain can affect sleep, leading to poor fatigue and further decline in quality of life.
4. Economic Cost
Secondary expenses include medical care, therapies, and lost earnings from reduced productivity.

Arthritis Management
Arthritis is incurable, but there are many uses that could be made for symptomatic management and enhancement of quality of life.
1. Drug Therapy
NSAIDs: Such as Ibuprofen, and Naproxen (example)-reduce pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroids such as PrednisoneHydrocortisone reduceeduce inflammation, and even suppress the body’s own immune response.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)-primarily used in rheumatoid arthritis medications help slow the progression of the disease.
Biologics-a class of the newest DMARDs-targeted therapy to specific parts of the immune system
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy programs can be designed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
3. Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists can help you learn to function more easily in daily activities that are less painful.
4. Surgery
For acute injury, there may be a need for surgical intervention, such as repair, replacement, or fusion of a joint.
5. Lifestyle Changes
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is ideal to reduce pressure on the joints.
Exercise: Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help maintain joint function and prevent stiffness.
Diet: A generally balanced diet holds anti-inflammatory nutrition in the type which includes fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids-can lead to a general feeling of well-being.
Home Remedies for Arthritis
Besides medical treatments, some home remedies can even soothe the symptoms of arthritis:
1. Heat and Cold Therapy
Hot Therapy: Putting up heating pads or taking warm baths may help relax muscles and improve blood circulation.
Cold Therapy: Use ice packs on the swollen region in order to reduce swelling and decrease pain.
2. Epsom Salt Baths
Bath in warm water with added Epsom salt. This also has magnesium, which may reduce inflammation and pain in the process.
3. Turmeric and Ginger
Turmeric and ginger are natural anti-inflammatory agents. Use these spices and supplements for possibly treating, or reducing arthritis symptoms.
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are acids found in fish oil, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These could help lessen joint pains and stiffness.
5. Acupuncture
Some of the sufferers claim that if treated with acupuncture, the suffering from arthritis pain would be somewhat relieved. Acupuncture is one of the methods used in traditional Chinese medicine where fine needles are used in puncturing particular points on the body to treat ailments.
6. Meditation and Yoga
Mindfulness practices such as meditation and yoga reduce pain and promote emotional comfort.
7. Hydration
Lubrication of the joints would depend on proper hydration. The right amount of fluids facilitates the smooth movement of fluid in the joints.
General Dietary Guidelines
For a diet plan that addresses the symptoms of arthritis, there should be anti-inflammatory foods that provide relief from the inflammation and discomfort plus work for general well-being. Here is an all-rounded diet plan for people with arthritis:
- Focus on Whole Foods: These are foods without much processing, which essentially have lots of nutrition.
- Hydration: One should drink plenty of fluids during the day.
- Balance Macronutrients: Proper amount of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
- Reduce Inflammatory Foods: Limit sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats.
Sample Diet Plan for Arthritis
Breakfast
Oatmeal with Berries:
1 cup cooked oatmeal topped with a handful of mixed berries (blueberries, strawberries) and a sprinkle of chia seeds.
Benefit: Whole grains give fiber; berries have antioxidants as well as anti-inflammatory compounds. Green tea instead of coffee, which is rich in antioxidants.
Midday Snack
Greek Yogurt with Honey and Walnuts:
1 cup low-fat Greek yogurt topped with a teaspoon of honey and a handful of walnuts.
Benefits: Yogurt contains probiotics for intestinal health, and walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Lunch
Quinoa Salad:
A quinoa bowl mixed together with cherry tomatoes, cucumber, bell peppers, and baby spinach; finished off with olive oil and lemon juice as dressing.
Benefits: Quinoa is a complete protein and high in fiber, and olive oil is anti-inflammatory.
Grilled Salmon:
4-6 ounces of grilled salmon, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Afternoon Snack
Carrot and Celery Sticks with Hummus:
Fresh vegetable sticks served with 2-3 tbsp of hummus.
Benefits: The vegetables contribute to vitamins and minerals, and hummus is an excellent source of protein and fiber.
Dinner
Stir-fried vegetables with Chicken:
Colorful mixed vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, and snap peas) stir-fried with skinless chicken breast in olive oil and garlic.
Good protein sources and plenty of fiber-rich vegetables.
Brown Rice or Sweet Potato
Typically: a serving of brown rice or baked sweet potato would mean complex carbohydrates and fiber.
Evening Snack (optional)
Chia Seed Pudding
Made with almond milk, topped with a few slices of banana or sprinkles of cinnamon.
Benefits: Chia seeds have a good amount of omega-3s, fiber, and antioxidants.
Dietary Inclusions
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables that are to be consumed in abundance include berries, cherries, oranges, spinach, and broccoli.
- Whole Grains: Good inclusion is brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-grain bread.
- Healthy Fats: Including olive oil, avocados, nuts like walnuts and almonds, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel.
- Lean Proteins: A good source would be skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and beans.
- Herbs and Spices: Turmeric and ginger are perfect with anti-inflammatory properties.
Foodstuffs to Avoid
- Refined Sugars: Candy, soda, and cookies.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, cakes, and processed carbohydrates
- Saturated Fats: Red meat and full-fat dairy.
- Trans Fats: Often found in fried foods and commercially baked goods.
- Too Much Salt: Many processed foods are high in sodium.
More Tips
- Supplement: Omega-3 supplements or turmeric capsules may also be beneficial, but of course, you first need a doctor’s green light.
- Keep a diary of what you eat, or maintain a food diary to determine which food may cause or exacerbate the symptoms of inflammation.
- Consult a Nutritionist. A registered dietitian can provide personal guidance on diet, based on your health, health needs, and preferences.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a complex disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This ailment heightens instances of pain and stiffness in the joints, while it also diminishes someone’s quality of life. Knowing the symptoms, causes, and treatment methods is essential to this condition’s proper handling. While curative and palliative medical measures are greatly needed, lifestyle modification and natural remedies can become considerably helpful in reducing symptoms. Thus, if you think that you are suffering from arthritis or having some form of joint pain, you have to see a doctor for proper diagnosis and management. People with arthritis can lead a fulfilling life despite all the adversities that come with it if approached with the right attitude.