PCOD is a condition in which ovaries produce many immature or partially mature eggs, this happen due to poor lifestyle, obesity, stress and hormonal imbalance. PCOS is a metabolic disorder and more severe form of PCOD can lead to anovulation where ovaries stop releasing eggs. Worldwide, many women are affected by the disorders polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and polycystic ovary disease (PCOD), which lead to hormonal and metabolic abnormalities.
Understanding PCOS and PCOD and knowing how to properly manage them are crucial given the rising prevalence of these illnesses. This comprehensive guide will examine the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, with a focus on dietary and lifestyle modifications that can significantly improve the lives of individuals who are affected.
Knowledge about PCOS and PCOD
Multiple tiny ovarian cysts appear in both PCOS and PCOD, which disrupts hormone balance and raises the risk of a number of health problems like diabetes, acne, infertility, and excessive hair growth. Although there is no specific treatment for these illnesses, many women have reported considerable improvements as a result of lifestyle changes and non-traditional therapies.
Insulin’s Function in PCOS and PCOD
The pancreas-secreted hormone insulin is essential for controlling blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance develops when people with PCOS or PCOD frequently have higher insulin levels than normal. When the body has trouble using insulin properly, it develops insulin resistance, which forces the pancreas to generate extra insulin as a coping mechanism. This extra insulin can cause hormonal imbalances and the symptoms of PCOS and PCOD by causing the ovaries to generate more androgens, such as testosterone.
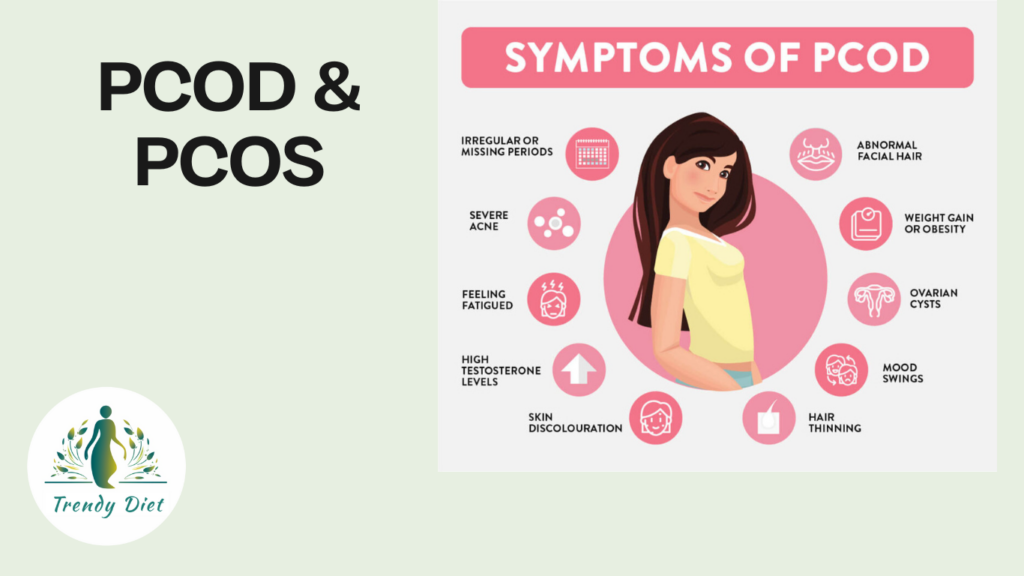
Common PCOS and PCOD symptoms
The symptoms of PCOS and PCOD can take many different forms, with irregular periods being one of the more prevalent ones. Diabetes, infertility, acne, weight gain, oily skin, migraines, excessive hair growth, and cardiovascular issues are examples of further symptoms. Additionally, some people may also experience sadness and mood fluctuations. It’s crucial to remember that not all PCOS and PCOD sufferers will present with the same symptoms, and some cases may go unnoticed if there are no irregular periods present.
Dietary Influence on PCOS and PCOD
In order to control the symptoms of PCOS and PCOD, diet is essential. Making the appropriate meal choices can promote weight control, enhance overall hormonal balance, and help regulate insulin levels. Consider these nutritional recommendations:
1. Emphasize complex carbohydrates and foods with a low glycemic index.{PCOS diet plan}
It is possible to minimize insulin resistance and stabilize blood sugar levels by eating more complex carbs and choosing foods with a low glycemic index. Include whole grains in your meals, such as quinoa, brown rice, and oats. White bread, pastries, and sugary snacks should not be consumed since they contain refined carbs, which might increase insulin resistance.
2. Include foods high in fiber
Foods high in fiber can improve digestion, control blood sugar levels, and increase feelings of fullness. Include a lot of whole grains, legumes, fruits, and veggies in your diet. Fruits like berries, oranges, peaches, and watermelons are good choices, and dark-green leafy vegetables like broccoli and lettuce are a powerhouse of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
3. Decide on lean proteins
Choose skinless chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and lentils as your lean protein options. These proteins can preserve muscle mass while assisting in weight management because they are low in saturated fats.
4. Avoid trans and saturated fats.{pcos foods to avoid}
Insulin resistance might increase and inflammation can be exacerbated by trans and saturated fats. Red meat, processed meats, and full-fat dairy products are foods to avoid since they are high in saturated fats. Choose the healthy fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
5. Steer clear of sugary beverages and added sugars
Sugar addition can raise blood sugar levels and cause weight gain. Limit the amount of sweet snacks, sweets, and beverages you consume. Be cautious of hidden sugars in processed foods and choose natural sweeteners sparingly, such as stevia or honey.
6. Drink plenty of water and avoid caffeine
Constipation and water retention, which are typical issues for people with PCOS and PCOD, can be avoided by drinking enough water, which is important for overall health. Limit your use of caffeinated beverages because they may interfere with hormone regulation.
7. Include inflammatory-fighting foods and spices
The symptoms of PCOS and PCOD may be lessened by some foods and spices that have anti-inflammatory qualities. Include meals like salmon and sardines as well as fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, as well as spices like cinnamon, ginger, and turmeric.
8. Pay Attention to Portions
It’s crucial to keep your weight in check if you want to manage PCOS and PCOD. Consider your portion proportions and try not to overeat. By paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, practice mindful eating.
9. Take into account dietary supplements
If you’re unsure about whether nutritional supplements are right for you, speak with a qualified dietician or a member of the medical profession. Omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and chromium supplements have demonstrated promise in the treatment of PCOS symptoms.
10. Consult a professional for advice
It is significant to remember that each person is unique, and that they may have different dietary requirements. A licensed dietitian with experience in PCOS and PCOD can offer you individualized advice and make sure you’re getting the nutrition you need.
Changing Your Lifestyle
Incorporating specific lifestyle adjustments can help PCOS and PCOD management in addition to food changes. Here are some ideas to think about:
1. Be Physically Active Frequently
Regular exercise has been demonstrated to alleviate PCOS and PCOD symptoms, help with weight management, and increase insulin sensitivity. Aim for 150 minutes or more per week of moderately intense aerobic activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Include weightlifting activities to increase muscular mass and metabolism.
2. Control your stress level
The symptoms of PCOS and PCOD can worsen under stress. Try stress-relieving routines like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or writing. To manage stress and enhance general well-being, think about getting help from a therapist or counselor.
3. Put sleep first
The balance of hormones and general health depend on getting enough sleep. Spend 7-9 hours each night getting a good night’s sleep. Create a relaxing setting for sleeping, establish a nightly ritual, and avoid using electronics just before bed.
4. Give up smoking
Smoking can exacerbate PCOS and PCOD symptoms and raise the risk of a number of health issues. If you smoke, think about getting help from a professional or joining a support group to stop permanently.
5. Maintain Knowledge and Practice Self-Care
Learn about PCOS and PCOD, and keep up with the most recent findings and available therapies. Take part in self-care practices that enhance relaxation and wellbeing, such as taking a warm bath, meditating, or engaging in a favorite hobby.
Looking for Expert Advice
Working closely with healthcare specialists, such as gynecologists, endocrinologists, registered dietitians, and mental health professionals is vital even though lifestyle changes can significantly affect controlling PCOS and PCOD. They can give you individualized advice, keep track of your development, and suggest the best course of action depending on your particular requirements.
Keep in mind that managing PCOS and PCOD calls for tolerance and reliability. You may take charge of your health and enhance your general well-being by adopting a healthy lifestyle, making wise eating decisions, and getting professional advice.
